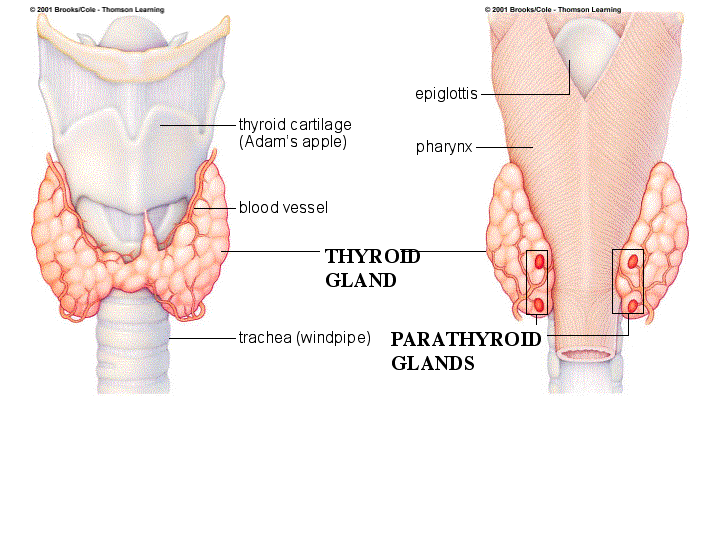
Pregnancy and postpartum are transformative periods in a woman’s life, filled with joy, anticipation, and often, unexpected challenges. Among the many changes your body undergoes, your thyroid health plays a crucial yet often overlooked role. The thyroid gland, responsible for regulating metabolism and energy levels, becomes even more vital during pregnancy as it supports your baby’s development and your body’s increased metabolic demands.
For women with existing thyroid conditions or those at risk of developing them, understanding how to manage and monitor thyroid function during these stages is essential. Whether it’s optimizing your levothyroxine dosage calculator results, recognizing symptoms of imbalance, or adopting thyroid-friendly habits, taking proactive steps can make all the difference for both you and your baby.
Tips for Maintaining Thyroid Health During Pregnancy
Monitor Thyroid Hormone Levels Regularly
Pregnancy can significantly alter thyroid hormone levels, making regular monitoring essential. Your doctor may recommend blood tests to measure TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and T4 levels at various stages of pregnancy. If you’re taking levothyroxine, ensure your dosage is adjusted as needed based on your levothyroxine dosage calculator results and medical advice. Keeping your hormone levels balanced is crucial for both your health and your baby’s development.
Ensure Adequate Iodine Intake
Iodine is a key nutrient for thyroid function, particularly during pregnancy. It supports the production of thyroid hormones and helps prevent developmental issues in your baby. To ensure adequate iodine intake, incorporate iodine-rich foods such as:
- Dairy products
- Fish and seafood
- Iodized salt
If necessary, your doctor may recommend an iodine supplement tailored to your needs. However, avoid excessive intake, as too much iodine can also negatively impact thyroid function.
Focus on a Thyroid-Supportive Diet
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients plays a crucial role in maintaining thyroid health. Some key nutrients to focus on include:
- Selenium: Found in Brazil nuts and sunflower seeds, selenium helps protect the thyroid from oxidative stress and supports hormone production.
- Zinc: Present in lean meats, beans, and nuts, zinc is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Vitamin D: Important for immune function and thyroid regulation, vitamin D can be obtained through sunlight exposure or fortified foods.
Additionally, be mindful of excessive consumption of goitrogens—naturally occurring substances found in raw cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, kale, and cabbage—which may interfere with thyroid hormone production if consumed in large amounts. Cooking these vegetables can help reduce their impact.
Manage Stress Levels
High stress can disrupt thyroid function by elevating cortisol levels, which can interfere with hormone production and lead to further imbalances. To maintain hormonal balance, incorporate stress-relieving practices such as:
- Yoga and meditation
- Prenatal massage
- Deep breathing exercises
Take Medications as Prescribed
If you have hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, adhering to your prescribed medication regimen is vital. For those on levothyroxine, taking the medication correctly is essential for proper absorption. Follow these guidelines:
- Take it on an empty stomach, at least 30–60 minutes before eating.
- Avoid calcium or iron supplements within four hours of taking your medication.
- Stick to the same brand of medication whenever possible to prevent fluctuations in hormone levels.
Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your dosage or experience any unusual symptoms.
Tips for Postpartum Thyroid Health
Be Aware of Postpartum Thyroiditis Symptoms
Postpartum thyroiditis, an inflammation of the thyroid gland, can develop in the months following childbirth. This condition often presents in two phases:
- Hyperthyroid phase: Symptoms may include anxiety, rapid heartbeat, irritability, and unexplained weight loss.
- Hypothyroid phase: Symptoms can include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and difficulty concentrating.
Continue Regular Thyroid Monitoring
Hormonal fluctuations during the postpartum period can contribute to thyroid imbalances, which is why regular check-ups with your healthcare provider remain essential. Blood tests to measure thyroid function may be recommended at various intervals to detect any emerging issues before they become severe.
Prioritize Sleep and Recovery
While the demands of caring for a newborn can make sleep elusive, prioritizing rest is crucial for thyroid health. Sleep deprivation can increase stress hormones, which may negatively impact thyroid function. Consider the following strategies to improve sleep quality:
- Ask for help from family or friends to share caregiving responsibilities.
- Create a sleep schedule with your partner to ensure you get adequate rest.
- Take short naps when the baby sleeps to catch up on lost sleep.
Maintain a Nutrient-Dense Diet
Postpartum recovery requires a diet rich in essential nutrients to support your thyroid and overall health. Some key dietary considerations include:
- Iron: Essential for energy production and found in foods like red meat, spinach, and legumes.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Support brain function and reduce inflammation; found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Antioxidants: Help combat oxidative stress; found in berries, leafy greens, and nuts.
Seek Support for Mental Health
Postpartum depression and anxiety are common but often overlooked contributors to thyroid imbalance. The thyroid and mental health are closely linked, and untreated mental health conditions can exacerbate thyroid issues. If you feel overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek support from a therapist or counselor specializing in postpartum care. Joining a support group or talking with other new mothers can also provide emotional reassurance and practical advice.
The Role of Your Healthcare Team
Maintaining thyroid health during pregnancy and postpartum requires a collaborative approach. Work closely with your healthcare provider to:
- Adjust medication dosages as needed based on regular testing.
- Develop a tailored nutrition and exercise plan to support thyroid function.
- Address any symptoms or concerns promptly to ensure optimal health for you and your baby.
Final Thoughts
Your thyroid plays a pivotal role in supporting a healthy pregnancy and postpartum recovery. By prioritizing regular monitoring, maintaining a thyroid-supportive diet, and managing stress, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your thyroid health. Every woman’s journey is unique, so consult with your healthcare provider to create a personalized plan that works for you. With the right care and attention, you can navigate this transformative period with confidence and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How often should I check my thyroid levels during pregnancy?
It’s recommended to check thyroid levels every 4–6 weeks or as advised by your doctor. - Can postpartum thyroiditis go away on its own?
Yes, in many cases, it resolves within a year, but some women may need long-term treatment. - What foods should I avoid for better thyroid health?
Limit raw cruciferous vegetables, excessive soy, and highly processed foods that may disrupt thyroid function.